Howard-Yana Shapiro is global director of plant science and external research for Mars, the secretive food/confectionary empire. He sports a mesmerizing long white beard, which dates back beyond a decade of corporate life to when he founded a radical organic food company, Seeds of Change.
Twelve years after Seeds of Change was sold to Mars — amid cries of betrayal from some customers — Shapiro recently announced that the world’s biggest chocolate company is committing itself to sustainable sourcing of the whole of its annual cocoa bean supply, worth more than US$1 billion. The policy starts with the Galaxy bar and by 2020 will encompass not just Galaxy and Mars but also Snickers, Twix and M&Ms. The new strategy also covers environmental issues and labor, dwarfing Cadbury’s pledge that all Dairy Milk chocolate will be Fairtrade later this year.
Shapiro’s visit to London was a chance to try and find out why Mars had made such an ambitious pledge.
Was this an example of a mega-business being influenced from within by its smaller, chippier acquisition? Or would Mars have done this anyway, for purely commercial reasons?
“If you want to set the stakes [higher] you can’t say ‘this is good, this is bad,’” Shapiro says. “Let’s make everything good, let’s take our profitability and go out and certify 100 percent of our cocoa globally.”
Mars bought Seeds of Change because it saw a future in ethical production, Shapiro says. Crucially, however, Mars had the might to put those principles into practice on a much bigger scale.
“If you’re interested in the future, scale is one of the things that’s critical,” Shapiro says. “I’m interested in not having any hungry people in the world. I’m interested in changing the lives of as many people as possible.”
Shapiro set up Seeds of Change in the late 1980s as an organic seed producer. At first, the company was more activist than commercial. Shapiro had learned about farming from his extended family; his parents came from Russia and Lithuania to the US before he was born. His father was a chemist and physicist who worked in academia and industry and taught him to think “systematically.” His mother, he says, “taught me abstract thinking.” The family did math problems instead of games on car journeys.
“From a very, very early age, I had an understanding of what complexity was,” he says.
Shapiro’s first love was flowers, and he thinks, but is not sure, that his first experiment on plant breeding was with African violets. Later he “realized it was food I was really interested in.”
In 1997, Seeds of Change wanted to expand into now popular foods such as pasta and sauce. It looked around for a commercial partner and sold itself to Mars. Shapiro says what was important was Mars’ “five principles”: quality, responsibility, mutuality, efficiency and freedom — that is, freedom from public ownership.
“They understood what we stood for, and shared the same views, though they used different ways,” he says.
Since he joined Mars, Shapiro appears to have thrived. He heads a team of a few dozen full-timers and more outside experts, from where, he says, he is “two steps, or one step” from where decisions are made at the top.
In moving up the closed, family-dominated petfood-to-confectionary group, Shapiro has swapped his biker gear for a suit and uses phrases such as “freedom works with profitability.” But he still has his signature beard and a calm, infectious passion for his work. From these clues it is tempting to try and work out what compromises the radical hippy and his pioneering seed company had to make, and whether they were worth it.
About 18 months ago Ethical Consumer magazine gave “before” and “after” scores to brands that had been sold to corporations. Like many of the acquisitions, Seeds of Change did badly, dropping from 15 to 3.5 out of 20. This Easter the UK-based magazine ranked chocolate eggs. Again, two Mars brands — Mars and Galaxy — did badly, scoring a near-bottom three out of 20. The company was marked down for poor environmental reporting, testing on animals, operations in oppressive regimes and campaigning against EU obesity laws.
Shapiro dismisses Ethical Consumer’s criticism, arguing: “We’re a private company — it would be hard for them to know anything about us.”
Instead, he points out major policy developments. Last June Mars announced it would contribute US$10 million to a project to map the cacao tree genome and publish it for free to speed up the development of quicker-growing and more resilient varieties. In November the company sponsored a major conference of nongovernmental organizations and governments to develop a 30-year plan to encourage cocoa growers in Africa to plant different crops to restore nutrients to degraded soil and bring a year-round income.
This was background to the announcement last month that the Rainforest Alliance and at least five other global certification bodies will be asked to make sure all cocoa beans bought by Mars meet standards such as a minimum wages for farmers, conserving water and biodiversity-friendly pest management.
“Mars’ commitment to buying sustainable cocoa is unprecedented, and the benefits to farmers, farm workers, tropical environments and wildlife will be tangible,” said Tensie Whelan, president of the Rainforest Alliance.
Shapiro says changes Mars has made — the genome mapping, the survival plan, the insistence on fair pay and good environmental practices — are crucial to its future because the company cannot thrive if such an important part of its supply chain is suffering.
“How can you expect to keep extracting out of soil if you don’t put something in?” he says.
With three years of global cocoa deficits and warnings that production is reaching its upper limits, coupled with the threat of climate change to growing patterns and evidence that shoppers want a wider variety of ethically certified goods, shoring up supply chains seems good business sense, even without the social and environmental considerations.
“The whole industry is going this way,” Shapiro says.
Unlike many companies, Mars can take this long-term view, he says.
“We want to be in business in 100 years. You don’t spend money like this short term. We’re thinking about these actions for the grandchildren of the owners,” he says.

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
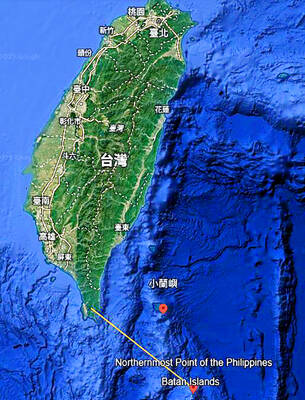
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College