Phishing scams have grown up from the unsophisticated swindles of the past in which fake Nigerian princes e-mailed victims, who were told they would get a big windfall if they just provide their bank account number.
Even as authorities try to stamp out that con and other e-mail and online scams, scammers are getting more wily and finding new loopholes to exploit.
The vast majority of e-mail is spam and an unknown percentage of that is meant to defraud. The scale of electronic fraud means that the criminals can make huge profits even if only a small percentage of people are duped.
Phishing commonly refers to hoax e-mails purportedly from banks or other trustworthy sources that seek to trick recipients into revealing bank or credit card account numbers and passwords.
The US government scored a big victory in November when the Web hosting company McColo Corp was taken offline. Estimates vary, but the Washington Post said that 75 percent of spam worldwide had been sent through that single company.
But the spam e-mails offering celebrity diets, cheap printer ink, erased credit card debt and amazing orgasms found a new way to inboxes, according to Google’s security subsidiary Postini.
Now spammers use a variety of computers to send out spam e-mails to obscure their origins, meaning that a dramatic McColo-style takedown will be harder to reproduce, said Adam Swidler, product marketing manager for Google’s Postini.
And they’ve largely abandoned scams that are easy to see through — like the Nigerian prince — in favor of sophisticated “location-based spam,” which directs the victim to a Web site discussing a local disaster or similar issue. If they click on the offered video, the Web site downloads a virus to the user’s computer, Google said in a blog on security.
Tim Cranton, a Microsoft cybersecurity expert, said there was no way to know how much money is stolen.
“We don’t have a way to estimate numbers because there are so many victims that you’re not aware of,” he said.
E-con artists are getting more sophisticated in approaching potential victims. One tactic has been to write spam that purports to come from a trusted source, like Paypal.
When Paypal, which is owned by eBay, learned that spammers were using its name, they put a digital signature on their e-mails and asked providers like Yahoo and Google to block any e-mail purporting to come from them that did not have that signature.
“We know how many they throw away and it’s approximately speaking about 10 million a month,” said Michael Barrett, Paypal’s chief information security officer. “If the consumer never sees the e-mail in the first place then it’s hard for them to get victimized.”
“Phishing was not just impacting consumers, in terms of general loss, it was impacting their view of the safety of the Internet and … indirectly damaging our brand,” he said.
Security experts say they are seeing more and more shifts from outright fraud, where the victim will hand over their money, to the use of malware, basically malicious software that, among other things, collects passwords and credit card numbers for thieves.
“Those will then be sold on the underground market,” said David Marcus, a threat research expert at McAfee computer security firm.
The person purchasing the passwords and card numbers will use that information to make purchases, get cash or create fake identities. The Federal Bureau of Investigation, working with police in the UK, Turkey and Germany, shut down one such online forum called Dark Market last October that, at its peak, had more than 2,500 registered members, the FBI said at the time.
But experts agreed that they didn’t expect the problem to go away anytime soon and that more people out of work could mean more people falling for scams.
Marcus said many of the scams were nothing more than the digital equivalent of confidence tricks, although on a massive scale that could net some scammers more than US$100,000 a month.
“These things only have to be 2 percent successful,” he said. “Those campaigns are sent out to tens of millions of people at the same time.”
Also See: The GhostNet in the machine

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
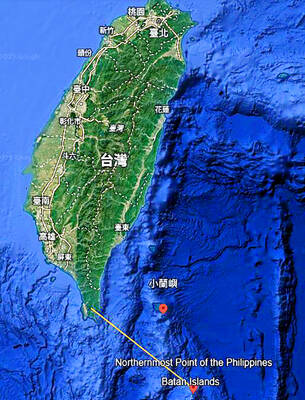
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College