There is a deafening, unearthly howl as if a jumbo jet was firing up its engines in London's Albert Hall. On the screen in the control room a ghostly pinkish glow whips round the edges of the inside of the nuclear reactor. At its core it is 10 times hotter than the center of the sun.
This, according to some physicists, is the solution to the energy crisis -- a future with cheap, reliable, safe and nearly waste-free power. Today, after years of false starts and political wrangling dating from the Cold War, they will get their chance to make that dream a reality. A 10 billion euro (US$12.74 billion) project, called Iter, to build a prototype nuclear fusion reactor will be signed off in Brussels by the EU, Japan, China, South Korea, India and the US.
The prospect of virtually limitless energy is not merely science fiction. The haunting, screaming growl of matter being smashed together at unimaginably high speed is a daily occurrence at Jet in Oxfordshire, an existing experimental fusion reactor. Jet is by far the biggest of the world's 28 fusion reactors. It is the work of scientists here that has paved the way for the much bigger Iter, which, once the project is ratified in December, will be built in Cadarache in southern France.
Its advocates say nuclear fusion is the most promising long-term solution to the energy crisis, offering the possibility of abundant power from cheap fuel with no greenhouse gases and low levels of radioactive waste. But critics say the UK government is gambling huge sums of money -- 44 percent of it's research and development budget for energy -- on a long shot with no guarantee of ever producing useful energy.
Last week British Prime Minister Tony Blair backed conventional nuclear power, saying in a speech to business leaders that not replacing Britain's aging nuclear power stations would be "a serious dereliction of our duty to the future of this country."
He argued that only nuclear energy could prevent a huge hike in CO2 emissions once the current nuclear stations were decommissioned.
But while the debate over the future of conventional nuclear power continues, many physicists argue that fusion is the future.
"Fusion works -- it powers the sun and stars," said Sir Chris Llewellyn Smith, head of the UK Atomic Energy Authority. "In the second part of the century I'm optimistic it will indeed be a major part of the world energy portfolio."
Unlike nuclear fission, which tears atomic nuclei apart to release energy, fusion involves squeezing the nuclei of two hydrogen atoms together. This process releases a helium nucleus and a neutron plus huge quantities of energy. The hydrogen fuel is part heavy hydrogen or deuterium, which can be easily extracted from water, and part super-heavy hydrogen or tritium, which can be made from lithium, a reasonably abundant metal.
The energy produced is truly colossal. The lithium in just one laptop battery and the heavy hydrogen from half a bath of water could provide enough energy for the average European for 30 years.
One of fusion's big advantages over fission is safety. Firstly, there is no chance of a runaway meltdown as happened at Chernobyl. If you stop applying the fuel or switch off the magnetic jacket that keeps the fuel in the reactor, the reaction just stops.
"It is very difficult to keep it running. It is like keeping honey on the back of a spoon," said Mathias Brix, a physicist at Jet.
Also, the quantities of fuel involved are much smaller than in fission reactors. Jet contains less than a gram of fuel, while Chernobyl had 250 tonnes. Lastly, the fuel and waste from the reactor is much less radioactive. But although physicists think they understand fusion, harnessing it has proved extremely difficult.
Research first began in the 1950s with claims that fusion would provide reliable power by the end of the century but even now scientists admit that a commercial application is at least 40 years away. The problem is getting two nuclei close enough to fuse and then controlling the reaction. This means putting in huge amounts of energy at the start to convert less than a gram of the fusion fuel into a super-hot gas or plasma. Hydrogen nuclei flying around at high speed in the plasma can then come close enough together to fuse.
In 1991 Jet was the first fusion reactor to do this using a mixture of deuterium and tritium. It proved that fusion reactors could work, but was not a viable energy option because it only pumped out about 70 percent of the energy required to start the process off.
"The purpose of these experiments is not really to produce energy but to learn how to control the hot gas," Smith said.
Iter will be 10 times the volume of Jet and produce 10 times the energy needed to get the reaction started.
"It's the step where we will demonstrate scientifically and technically that fusion energy is a viable energy source," said Akko Mass, one of the Iter scientists.
But with so many broken promises some involved in the project doubt it will yield commercial energy any time soon. Iter scientist John How described the billed 40-year timescale as "very, very, very ambitious." He suspects it will be nearer to a century.

ENDEAVOR MANTA: The ship is programmed to automatically return to its designated home port and would self-destruct if seized by another party The Endeavor Manta, Taiwan’s first military-specification uncrewed surface vehicle (USV) tailor-made to operate in the Taiwan Strait in a bid to bolster the nation’s asymmetric combat capabilities made its first appearance at Kaohsiung’s Singda Harbor yesterday. Taking inspiration from Ukraine’s navy, which is using USVs to force Russia’s Black Sea fleet to take shelter within its own ports, CSBC Taiwan (台灣國際造船) established a research and development unit on USVs last year, CSBC chairman Huang Cheng-hung (黃正弘) said. With the exception of the satellite guidance system and the outboard motors — which were purchased from foreign companies that were not affiliated with Chinese-funded

PERMIT REVOKED: The influencer at a news conference said the National Immigration Agency was infringing on human rights and persecuting Chinese spouses Chinese influencer “Yaya in Taiwan” (亞亞在台灣) yesterday evening voluntarily left Taiwan, despite saying yesterday morning that she had “no intention” of leaving after her residence permit was revoked over her comments on Taiwan being “unified” with China by military force. The Ministry of the Interior yesterday had said that it could forcibly deport the influencer at midnight, but was considering taking a more flexible approach and beginning procedures this morning. The influencer, whose given name is Liu Zhenya (劉振亞), departed on a 8:45pm flight from Taipei International Airport (Songshan airport) to Fuzhou, China. Liu held a news conference at the airport at 7pm,
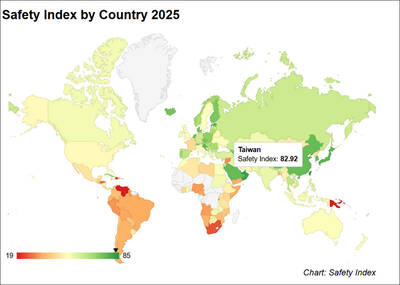
Taiwan was ranked the fourth-safest country in the world with a score of 82.9, trailing only Andorra, the United Arab Emirates and Qatar in Numbeo’s Safety Index by Country report. Taiwan’s score improved by 0.1 points compared with last year’s mid-year report, which had Taiwan fourth with a score of 82.8. However, both scores were lower than in last year’s first review, when Taiwan scored 83.3, and are a long way from when Taiwan was named the second-safest country in the world in 2021, scoring 84.8. Taiwan ranked higher than Singapore in ninth with a score of 77.4 and Japan in 10th with

GRIDLOCK: The National Fire Agency’s Special Search and Rescue team is on standby to travel to the countries to help out with the rescue effort A powerful earthquake rocked Myanmar and neighboring Thailand yesterday, killing at least three people in Bangkok and burying dozens when a high-rise building under construction collapsed. Footage shared on social media from Myanmar’s second-largest city showed widespread destruction, raising fears that many were trapped under the rubble or killed. The magnitude 7.7 earthquake, with an epicenter near Mandalay in Myanmar, struck at midday and was followed by a strong magnitude 6.4 aftershock. The extent of death, injury and destruction — especially in Myanmar, which is embroiled in a civil war and where information is tightly controlled at the best of times —