A global race is under way to reach the next milestone in supercomputer performance, many times the speed of today's most powerful machines.
And beyond the customary rivalry in the field between the US and Japan, there is a new entrant -- China -- eager to showcase its arrival as an economic powerhouse.
The new supercomputers will not be in use until the end of the decade at the earliest, but they are increasingly being viewed as crucial investments for progress in science, advanced technologies and national security.

PHOTO: NY TIMES
Once the exclusive territory of nuclear weapons designers and code breakers, ultrafast computers are increasingly being used in everyday product design. Procter & Gamble used a supercomputer to study the airflow over its Pringles potato chips -- to help stop them from fluttering off the assembly lines.
Today, driven by advances in so-called parallel computing -- with software making it possible to lash together arrays of tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of processor chips -- the speed of future supercomputers is limited only by cost, adequate electricity and the ability to cool the systems, which nowadays can sprawl over thousands of square meters.
China now has 19 supercomputers ranked among the 500 fastest machines, and recent reports in Chinese newspapers stressed the importance of developing high-performance computing technology not dependent on the US.
"It's becoming an issue of national pride," said Steve Wallach, a supercomputer designer who is a vice president at Chiaro Networks, a technology provider for high-performance computing. "That's where the Japanese are coming from, and now the Chinese want to be viewed as a Tier 1 country in every respect."
Indeed, in recent weeks there have been reports that both the Japanese and Chinese are planning new investments in breaking the petaflop computing barrier. A petaflop is a measure of computing performance that describes the ability to perform 1,000 trillion mathematical operations a second, roughly eight times the speed of today's fastest computer.
"Everyone appears to be in the race for a petaflop," said Jack Dongarra, a computer scientist at the University of Tennessee who maintains a list of the world's fastest computers.
Currently the world's fastest computer is a machine installed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory late last year -- and still growing -- that has reached more than 136 trillion operations a second, or 100,000 times the speed of a fast desktop personal computer. IBM built the machine, Blue Gene/L, and plans to double its speed before the end of the year.
Only small amounts of research funds have been spent so far on designing a petaflop supercomputer, an accomplishment that Japanese and American experts believe will cost nearly US$1 billion for each machine to achieve. But 10 companies have indicated that they are doing preliminary work, Dongarra said.
In the US, Cray, IBM and Sun Microsystems have begun work toward reaching a petaflop by the end of the decade, supported by a development project financed by the Pentagon.
The project, the High Productivity Computer Systems program of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, or DARPA, was begun in 2003 with about US$150 million as one of a series of US responses to the emergence of a Japanese supercomputer -- the Earth Simulator, intended for climate research -- as the world's fastest in 2002, displacing the US for the first time.
With significant financial support from the government, IBM, Cray and Silicon Graphics all built new massively parallel supercomputers, enabling the US to recapture world leadership in November last year.
As a result, in the most recent ranking of the world's 500 fastest computers, released in June, the US holds the top three positions. The Earth Simulator has fallen to fourth place, with about a quarter the computing speed of the new leader.
Some executives say they believe the US is well positioned to remain dominant in computing technologies.
"There is a lot less angst in the US than there was previously," said David Turek, vice president for high-performance computing at IBM. "We're not asleep at the switch."
But the fastest American machines are used primarily for military applications at the nation's weapons laboratories. Many scientists and technology executives in the US are concerned about losing out in crucial markets like oil and gas exploration, automobile design and manufacturing unless they, too, have access to the fastest supercomputers. They contend that a public-private partnership is needed to develop supercomputers whose applications are not limited to the military.
Not all supercomputer experts are convinced that having the world's fastest computer is essential to American competitiveness.
"IBM and Cray are doing a good job of ensuring that the US remains competitive in the high-performance computing market," said C. Gordon Bell, a Microsoft researcher and a former supercomputer designer.
Because the very largest computers are so difficult to program, their impact in the short term is relatively limited, he added.
But in April, the Japanese Automobile Manufacturers Association reported that the Earth Simulator had been used by automotive engineers to greatly increase the speed and resolution of car-crash simulations, potentially offering a significant reduction in development time for new car models.
That has alarmed some US industry executives, who argue that high-performance computing is now decisive in industrial competitiveness.
"This is a subtle but important change in the competitiveness game," said Suzy Tichenor, vice president for high-performance computing projects at the Council on Competitiveness in Washington.
Last month in China, Lenovo Group, which acquired IBM's personal computer business last year, said it would join in a Chinese effort to build a petaflop machine by 2010 as part of a five-year government plan to advance the country's computer technology. Separately, two other Chinese companies, Dawning and Galactic Computing, have indicated they intend to develop petaflop-scale systems.
A French military program, led by the French computer maker Bull, has plans to reach a petaflop in 2013.
And already there is discussion of frontiers beyond a petaflop. Several Japanese newspapers have reported in the last month that the Japanese government is expected to announce a commitment to developing a 10-petaflop supercomputer as a follow-up to the Earth Simulator.
Separately, the Japanese computer maker Fujitsu said last month that it planned a three-petaflop computer, and the director of the Earth Simulator told <
The system will employ two computers, one for rough calculations and another for more precise computing, providing more efficiency than today's massively parallel machines.
While the US has regained the lead in supercomputing achievement, its researchers have benefited unevenly. The armed forces and intelligence agencies have traditionally commanded the very largest computing systems here, for example, while other countries have devoted their speediest computers to other efforts, notably research on climate change.
"These machines can be used to answer questions that literally will mean the life or death of humanity," said Peter Freeman, assistant director for computer and information sciences and engineering for the National Science Foundation. "Currently the data the United States has at its disposal is not as good as what the Japanese have. It's a national strategy question."
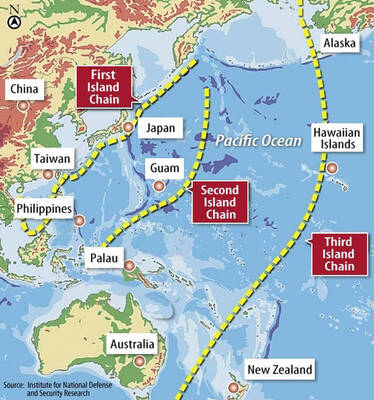
The US government has signed defense cooperation agreements with Japan and the Philippines to boost the deterrence capabilities of countries in the first island chain, a report by the National Security Bureau (NSB) showed. The main countries on the first island chain include the two nations and Taiwan. The bureau is to present the report at a meeting of the legislature’s Foreign Affairs and National Defense Committee tomorrow. The US military has deployed Typhon missile systems to Japan’s Yamaguchi Prefecture and Zambales province in the Philippines during their joint military exercises. It has also installed NMESIS anti-ship systems in Japan’s Okinawa

‘WIN-WIN’: The Philippines, and central and eastern European countries are important potential drone cooperation partners, Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung said Minister of Foreign Affairs Lin Chia-lung (林佳龍) in an interview published yesterday confirmed that there are joint ventures between Taiwan and Poland in the drone industry. Lin made the remark in an exclusive interview with the Chinese-language Liberty Times (the Taipei Times’ sister paper). The government-backed Taiwan Excellence Drone International Business Opportunities Alliance and the Polish Chamber of Unmanned Systems on Wednesday last week signed a memorandum of understanding in Poland to develop a “non-China” supply chain for drones and work together on key technologies. Asked if Taiwan prioritized Poland among central and eastern European countries in drone collaboration, Lin

NO CONFIDENCE MOTION? The premier said that being toppled by the legislature for defending the Constitution would be a democratic badge of honor for him Premier Cho Jung-tai (卓榮泰) yesterday announced that the Cabinet would not countersign the amendments to the local revenue-sharing law passed by the Legislative Yuan last month. Cho said the decision not to countersign the amendments to the Act Governing the Allocation of Government Revenues and Expenditures (財政收支劃分法) was made in accordance with the Constitution. “The decision aims to safeguard our Constitution,” he said. The Constitution stipulates the president shall, in accordance with law, promulgate laws and issue mandates with the countersignature of the head of the Executive Yuan, or with the countersignatures of both the head of the Executive Yuan and ministers or

CABINET APPROVAL: People seeking assisted reproduction must be assessed to determine whether they would be adequate parents, the planned changes say Proposed amendments to the Assisted Reproduction Act (人工生殖法) advanced yesterday by the Executive Yuan would grant married lesbian couples and single women access to legal assisted reproductive services. The proposed revisions are “based on the fundamental principle of respecting women’s reproductive autonomy,” Cabinet spokesperson Michelle Lee (李慧芝) quoted Vice Premier Cheng Li-chiun (鄭麗君), who presided over a Cabinet meeting earlier yesterday, as saying at the briefing. The draft amendment would be submitted to the legislature for review. The Ministry of Health and Welfare, which proposed the amendments, said that experts on children’s rights, gender equality, law and medicine attended cross-disciplinary meetings, adding that