Brazil plans to expand a crackdown on companies that patent products made from rare plants and animals without adequately compensating the South American country or its indigenous communities.
The fight against “biopiracy” has won the support of indigenous communities and defenders of the Amazon rain forest who say corporations unfairly benefit from medicine and other products derived from Brazil’s exotic plants, poisonous snakes or brightly colored frogs.
However, the effort has sparked criticism that it slows crucial scientific research and arbitrarily targets entrepreneurs that could develop environmentally sustainable businesses.
Brazil has levied more than 100 million reais (US$59 million) in fines since July on companies charged with not paying fair compensation for the use of genetic material native to Brazil, said Bruno Barbosa, who heads inspection for the environmental oversight agency Ibama.
Next year, officials will begin pursuing companies that did not notify the government of their use of local species to create products such as pharmaceuticals, as required by law, meaning fines will likely go up.
“Given that [fighting biopiracy] is a new process and that Brazil has one of the biggest reserves of biodiversity in the world, I think most of this activity is illegal, and we’re going to find those people,” he said.
Barbosa says examples of biopiracy abound, such as the development in the 1970s of the hypertension medication captopril from a snake venom that indigenous groups used on arrowhead tips.
Pharmaceuticals companies also used the yellow-and-green Kambo frog, found in Brazil’s Amazon state of Acre, to create anti-inflammatory drugs without distributing benefits to local residents, he said. Many of these incidents came before a 2001 decree that created the current rules governing species use.
The government this year stepped up the anti-biopiracy effort with a campaign known as “Operation New Direction” that aims to crack down on what it calls profiteering.
Fines next year may rise to US$29 million each and companies face possible cancelation of patents in Brazil if inspectors find they did not register the use of local species.
One of the biggest fines levied so far was on Brazil’s largest cosmetics maker Natura, Barbosa said. He declined to give details on the amount or the infraction because the process is ongoing.
Critics say Brazil’s often aggressive efforts to prevent biopiracy threaten to slow crucial scientific research that could provide new cancer treatments or remedies for diseases suffered by local populations.
They said it treats anyone interested in commercial use of rare species as possibly criminal, complicating government goals of developing research facilities near where the species are found to create jobs in those communities.
The government should make the rules clearer because the current system ends up penalizing those that make the most effort to be transparent about their use of genetic material, said Raul Telles do Valle who works with ISA, a think tank on social and environmental issues.
“The current law is very vague on a lot of points, it ends up classifying everybody as illegitimate,” he said. “Just passing out fines under the existing framework isn’t going to solve the problem.”
The law should reflect the difficulty of determining how to compensate local populations from collective knowledge passed down over generations, he said.
Barbosa says the government’s legislation is suitable and that expanding the fight against biopiracy could reduce the destruction of sensitive environments.
“This is going to enable concrete alternatives that substitute destruction of the ecosystem for new economic mechanisms,” he said.

Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (鴻海精密) yesterday said that its research institute has launched its first advanced artificial intelligence (AI) large language model (LLM) using traditional Chinese, with technology assistance from Nvidia Corp. Hon Hai, also known as Foxconn Technology Group (富士康科技集團), said the LLM, FoxBrain, is expected to improve its data analysis capabilities for smart manufacturing, and electric vehicle and smart city development. An LLM is a type of AI trained on vast amounts of text data and uses deep learning techniques, particularly neural networks, to process and generate language. They are essential for building and improving AI-powered servers. Nvidia provided assistance

GREAT SUCCESS: Republican Senator Todd Young expressed surprise at Trump’s comments and said he expects the administration to keep the program running US lawmakers who helped secure billions of dollars in subsidies for domestic semiconductor manufacturing rejected US President Donald Trump’s call to revoke the 2022 CHIPS and Science Act, signaling that any repeal effort in the US Congress would fall short. US Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer, who negotiated the law, on Wednesday said that Trump’s demand would fail, while a top Republican proponent, US Senator Todd Young, expressed surprise at the president’s comments and said he expects the administration to keep the program running. The CHIPS Act is “essential for America leading the world in tech, leading the world in AI [artificial
DOMESTIC SUPPLY: The probe comes as Donald Trump has called for the repeal of the US$52.7 billion CHIPS and Science Act, which the US Congress passed in 2022 The Office of the US Trade Representative is to hold a hearing tomorrow into older Chinese-made “legacy” semiconductors that could heap more US tariffs on chips from China that power everyday goods from cars to washing machines to telecoms equipment. The probe, which began during former US president Joe Biden’s tenure in December last year, aims to protect US and other semiconductor producers from China’s massive state-driven buildup of domestic chip supply. A 50 percent US tariff on Chinese semiconductors began on Jan. 1. Legacy chips use older manufacturing processes introduced more than a decade ago and are often far simpler than
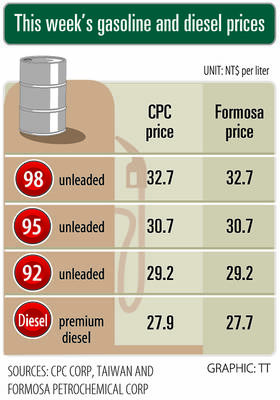
Gasoline and diesel prices this week are to decrease NT$0.5 and NT$1 per liter respectively as international crude prices continued to fall last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (CPC, 台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. Effective today, gasoline prices at CPC and Formosa stations are to decrease to NT$29.2, NT$30.7 and NT$32.7 per liter for 92, 95 and 98-octane unleaded gasoline respectively, while premium diesel is to cost NT$27.9 per liter at CPC stations and NT$27.7 at Formosa pumps, the companies said in separate statements. Global crude oil prices dropped last week after the eight OPEC+ members said they would