Russia's government may delay an agreement to supply crude oil and gas to China through pipelines because of domestic opposition, a Standard & Poor's report said.
Russian people are concerned that Chinese imports are threatening local industries and Russian President Vladimir Putin may not want to be seen to be increasing China's influence over his country, S&P's analysts, including Bei Fu in Hong Kong, wrote in a report on Wednesday.
China needs to secure oil and natural gas supplies to meet energy demand in an economy that grew 9.9 percent last year. Chinese President Hu Jintao (胡錦濤) wants an US$11.5 billion oil pipeline from eastern Siberia to the Pacific port of Nakhodka to include a spur to China, the world's second-biggest oil consumer.
The report said that, "Finding diverse and stable energy supplies such as from Russia, is critical for China over the long term."
Russia agreed in March to build two pipelines from the country's Pacific coast to China.
"Russia's new energy agreements with China are vague," the S&P report said. "No route or cost estimates have been given for the gas pipelines and only a sketchy timetable has been provided."
OAO Gazprom, Russia's largest gas producer, may export as much as 80 billion cubic meters a year of natural gas to China through the two new pipelines, Gazprom chief executive officer Alexei Miller said on March 21.
China National Petroleum Corp (
Under the agreement, the first pipeline will run 3,000km from western Siberia to China's western region, and the second from eastern Siberia to northeastern China, the S&P report said.
China in December raised factory prices for natural gas and changed its pricing mechanism of the fuel to move in line with demand in the local market.
By increasing prices, Beijing hoped to encourage companies to invest in gas plants, ensuring steady supply.
Prices for natural gas used by industries and city-gas distributors increased by between 50 yuan (US$6.19) and 150 yuan per thousand cubic meters, according to the Beijing-based National Development and Reform Commission, China's top economic planner, on Dec. 26.
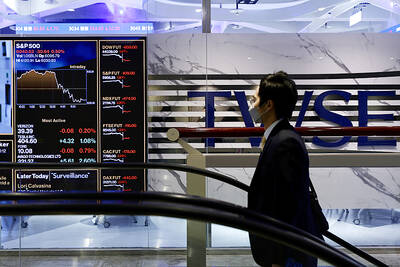
SELL-OFF: Investors expect tariff-driven volatility as the local boarse reopens today, while analysts say government support and solid fundamentals would steady sentiment Local investors are bracing for a sharp market downturn today as the nation’s financial markets resume trading following a two-day closure for national holidays before the weekend, with sentiment rattled by US President Donald Trump’s sweeping tariff announcement. Trump’s unveiling of new “reciprocal tariffs” on Wednesday triggered a sell-off in global markets, with the FTSE Taiwan Index Futures — a benchmark for Taiwanese equities traded in Singapore — tumbling 9.2 percent over the past two sessions. Meanwhile, the American depositary receipts (ADRs) of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電), the most heavily weighted stock on the TAIEX, plunged 13.8 percent in

A wave of stop-loss selling and panic selling hit Taiwan's stock market at its opening today, with the weighted index plunging 2,086 points — a drop of more than 9.7 percent — marking the largest intraday point and percentage loss on record. The index bottomed out at 19,212.02, while futures were locked limit-down, with more than 1,000 stocks hitting their daily drop limit. Three heavyweight stocks — Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電), Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (Foxconn, 鴻海精密) and MediaTek (聯發科) — hit their limit-down prices as soon as the market opened, falling to NT$848 (US$25.54), NT$138.5 and NT$1,295 respectively. TSMC's

TARIFFS: The global ‘panic atmosphere remains strong,’ and foreign investors have continued to sell their holdings since the start of the year, the Ministry of Finance said The government yesterday authorized the activation of its NT$500 billion (US$15.15 billion) National Stabilization Fund (NSF) to prop up the local stock market after two days of sharp falls in reaction to US President Donald Trump’s new import tariffs. The Ministry of Finance said in a statement after the market close that the steering committee of the fund had been given the go-ahead to intervene in the market to bolster Taiwanese shares in a time of crisis. The fund has been authorized to use its assets “to carry out market stabilization tasks as appropriate to maintain the stability of Taiwan’s

In a small town in Paraguay, a showdown is brewing between traditional producers of yerba mate, a bitter herbal tea popular across South America, and miners of a shinier treasure: gold. A rush for the precious metal is pitting mate growers and indigenous groups against the expanding operations of small-scale miners who, until recently, were their neighbors, not nemeses. “They [the miners] have destroyed everything... The canals, springs, swamps,” said Vidal Britez, president of the Yerba Mate Producers’ Association of the town of Paso Yobai, about 210km east of capital Asuncion. “You can see the pollution from the dead fish.